The Structure of the Nucleus Can Be Described as
Each shell can occupy a certain number of. The nucleus is usually filled with a vowel V because vowels are the most sonorous sounds.
Nucleus Definition Structure Parts Functions Diagram
Enclosed in a nuclear envelope.
. The shape of the nucleus varies from one cell to the next. Structure and Organization of the Nucleus. The nucleus may contain many lobes.
To then allow the nucleus to be the peak of sonority Consonants Cs being less sonorant flank the nucleus in the onset and coda positions. The structure of the nucleus consists of the following parts. Electrons are arranged around the nucleus in the shells of an atom.
The structure of the nucleus can be described as enclosed in a cell membrane enclosed in a nuclear envelope composed of cytoplasm composed of cytoplasmic organelles. First and foremost it is possible to duplicate ones DNA in the nucleus. Enclosed in a cell membrane.
Structure of Atom. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus centre in which the protons positively charged and neutrons neutral are present. If the nucleus is removed the cell dies.
The nucleus is a spherical-shaped organelle that is present in every eukaryotic cell. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is usually the most notable cell organelle in both size and function. An atom is a complex arrangement of negatively charged electrons organised in defined shells around a positively charged nucleus.
As such the nucleus includes a variety of structured aspects that permit it to perform its functions. There are exceptions which will be discussed later. At one extreme the nucleus has been proposed to have its own nucleoskeleton and distinct organelles.
The nucleus is a sphere-shaped organelle found in eukaryotic cells. First described by Brown in 1831 the cell nucleus is one of the best known but least understood of cellular organelles. The shells of an atom are numbered 12 3 and so on starting from the one closest to the nucleus.
The word nucleus stems from Latin and means kernel. It contains the genetic material of the cell in the form of nucleic acids. They can also look like pears or resemble a teardrop.
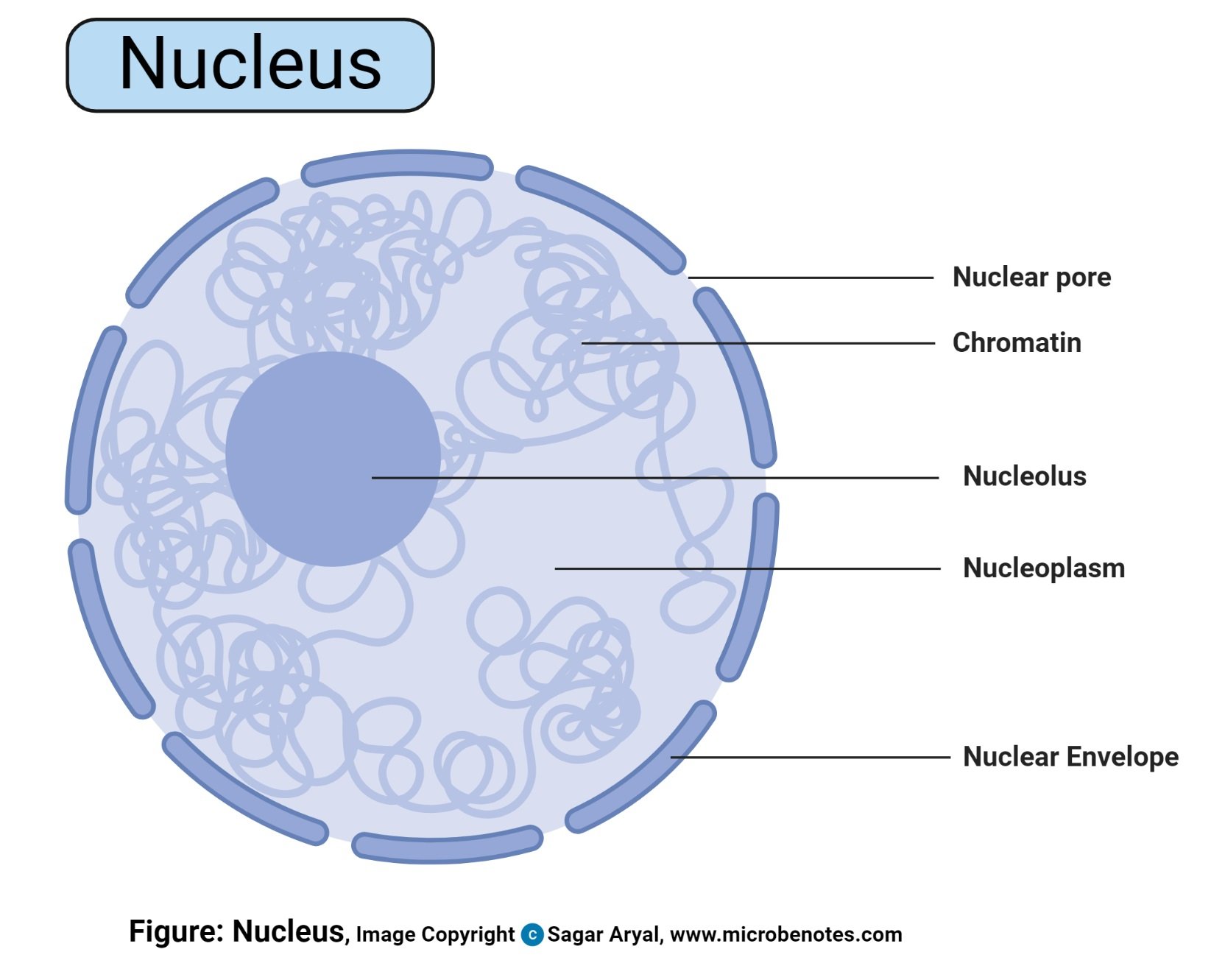
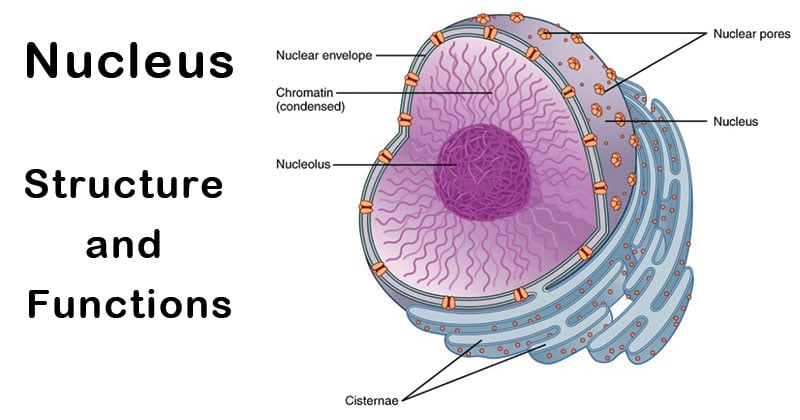
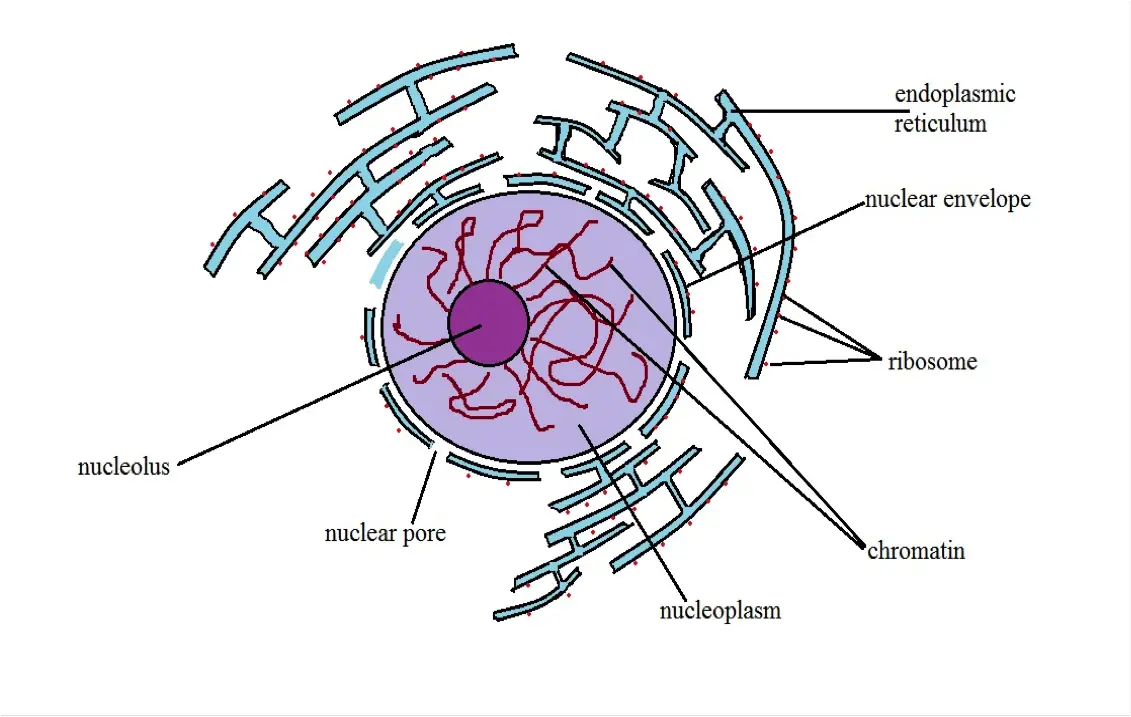
The nucleus contains most of the cells genetic material and is responsible for controlling the cells growth movement reproduction and eating. It is of the double- membrane and surrounds the nucleus. The structure of the nucleus includes nuclear membrane chromosomes nucleoplasm and nucleolus.
Every atom is roughly the same size. The nucleus could be described as bilobed multi-lobed or tri-lobed based on the amount of lobes. From Latin nucleus or nuculeus meaning kernel or seed is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cellsEukaryotes usually have a single nucleus but a few cell types such as mammalian red blood cells have no nuclei and a few others including osteoclasts have manyThe main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear.
The structure of a nucleus contains a nuclear membrane chromosomes nucleolus and cytoplasm. As the organelle that contains the genetic material of a cell the nucleus can be described as the command center. Structure of Nucleus.
111 is generally a round body occupying the centre of the cell. It is also responsible for the coordination of genes and gene expression. And contains a nuclear membrane chromosomes nucleolus and nucleoplasm.
As such the nucleus consists of a number of structured elements that allow it to perform its functions. White blood cells are an illustration one with lobed nucleus. The nucleus is composed of various structures namely nuclear envelope nucleoplasm or nucleus sap nuclear matrix chromatin and nucleolus.
Structure of the Nucleus As the organelle that contains the genetic material of a cell the nucleus can be referred to as the command center. Outer and inner membrane are present in it. The nucleus has been clearly explained as a membrane-bound structure that comprises the genetic material of a cell.
It is responsible for controlling all activities of the cell. Usually most mature cells possess a nucleus but there are certain larger cells in the body which may contain more than one nucleus. TorF the structure of the nucleus can be described as being enclosed in a nuclear envelope.
Its shape size position and number vary. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. According to the SSP the nucleus is the peak of sonority.
This nucleus which is made up of protons and neutrons contains the majority of the atoms mass except for common hydrogen which has only one proton. In most cases the nuclei are spherical or round. The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains a cells hereditary information and controls its growth and reproduction.
The structure of the nucleus can be described as a. The nuclear membrane forms an envelope like structure around the nuclear contents and is commonly known as a nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope separates the nucleoplasm from the cytoplasm.
In most eukaryotic cells the size of the nucleus ranges from 5 10 micrometers in diameter. The structure and functional organization of the nucleus remains a subject of energetic debate. It is a sphere-shaped organelle found in eukaryotic cells.
In cell biology the nucleus pl. Of all organelles in our cells the nuclei are the largest. It is not just a storage compartment for DNA but also happens to be the home of some important cellular processes.
The Electronic Structure of an Atom. The outer membrane of the nucleus is continuous with the ER Endoplasmic reticulum. This section gives focus to the structure of the cell.
The nucleus is the control centre of eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus Definition Structure Function Cellular Vs Atomic Nuclei

No comments for "The Structure of the Nucleus Can Be Described as"
Post a Comment